http://www.BioIngine.com
[healthcare cognitive computing platform]
Conquering Uncertainties Creating Infinite Possibilities
(Possible application :- Achieving Algorithm Driven ACO)
Introduction
The QEXL Approach is a Systems Thinking driven technique that has been designed with the intension of developing “Go To Market” solutions for Healthcare Big Data applications requiring integration between Payor, Provider, Health Management (Hospitals), Pharma etc; where the systemic complexities tethering on the “edge of chaos” pose enormous challenges in achieving interoperability owing to existence of plethora of healthcare system integration standards and management of the unstructured data in addition to structured data ingested from diverse sources. Additionally, The QEXL Approach targets for the creation of Tacit Knowledge Sets by inductive techniques and probabilistic inference from the diverse sets of data characterized by volume, velocity and variability. In fact, The QEXL Approach facilitates algorithmic driven Proactive Public Health Management, while rendering business models achieving Accountable Care Organization most effective.
The QEXL Approach is an integrative multivariate declarative cognitive architecture proposition to develop Probabilistic Ontology driven Big Data applications creating interoperability among Healthcare systems. Where, it is imperative to develop architecture that enable systemic capabilities such as Evidence Based Medicine, Pharmacognomics, biologics etc; while also creating opportunities for studies such as Complex Adaptive System (CAS). Such approach is vital to develop ecosystem as an response to mitigate the Healthcare systemic complexities. Especially CAS studies makes it possible to integrate both macro aspects (such as epidemiology) related to Efficient Heathcare Management Outcomes ; and micro aspects (such as Evidence Based Medicine and Pharmacogenomics that helps achieve medicine personalization) achieving Efficacy in the Healthcare delivery, to help achieve systemic integrity. In The QEXL Approach QEXL stands for “Quantum Exchange Language”, and Q-UEL is the initial proposed language. The QEXL Consortium embraces Quantal Semantics, Inc; (NC) and Ingine, Inc; (VA), and collaborates with The Dirac Foundation (UK), which has access to Professor Paul Dirac’s unpublished papers. The original consortium grew as a convergence of responses to four stimuli:
- The “re-emerging” interest in Artificial Intelligence (AI) as “computational thinking”, e.g. under the American Recovery Act;
- The President’s Council of Advisors on Science and Technology December 2010 call for an “XML-like” “Universal Exchange Language” (UEL) for healthcare;
- A desire to respond to the emerging Third World Wide Web (Semantic Web) by an initiative based on generalized probability theory – the Thinking Web; and
- In the early courses of these efforts, a greater understanding of what Paul Dirac meant in his Nobel Prize dinner speech where he stated that quantum mechanics should be applicable to all aspects of human thought.
The QEXL Approach
The QEXL Approach is developed based on considerable experiences in Expert Systems, linguistic theory, neurocognitive science, quantum mechanics, mathematical and physics-based approaches in Enterprise Architecture, Internet Topology, Filtering Theory, Semantic Web, Knowledge Lifecycle Management, and principles of Cloud Organization and Integration. The idea for well-formed probabilistic programming reasoning language is simple. Importantly, also, the more essential features of it for reasoning and prediction are correspondingly simple such that the programmers are not necessarily humans, but structured and unstructured (text-analytic) “data mining” software robots. We have constructed a research prototype Inference Engine (IE) network (and more generally a program) that “simply” represents a basic Dirac notation and algebra compiler, with the caveat that it extends to Clifford-Dirac algebra; notably a Lorentz rotation of the imaginary number i (such that ii = -1) to the hyperbolic imaginary number h (such that hh = +1) corresponding to Dirac’s s, and gtime or g5) is applied.
[Outside the work of Dr. Barry Robson, this approach has not been tried in the inference and AI fields, with one highly suggestive exception: since the late 1990s it has occasionally been used in the neural network field by T. Nitta and others to solve the XOR problem in a single “neuron” and to reduce the number of “neurons” generally. Also suggestively, in particle physics it may be seen as a generalization of the Wick rotation time → i x time used by Richard Feynman and others to render wave mechanics classical. It retains the mathematical machinery and philosophy of Schrödinger’s wave mechanics but, instead of probability amplitudes as wave amplitudes, it yields classical but complex probability amplitudes encoding two directions of effect: “A acts on B, and B differently on A”. It maps to natural language where words relate to various types of real and imaginary scalar, vector, and matrix quantities. Dirac’s becomes the XML-like semantic triple . ]
The QEXL Approach involves following interdependent components.
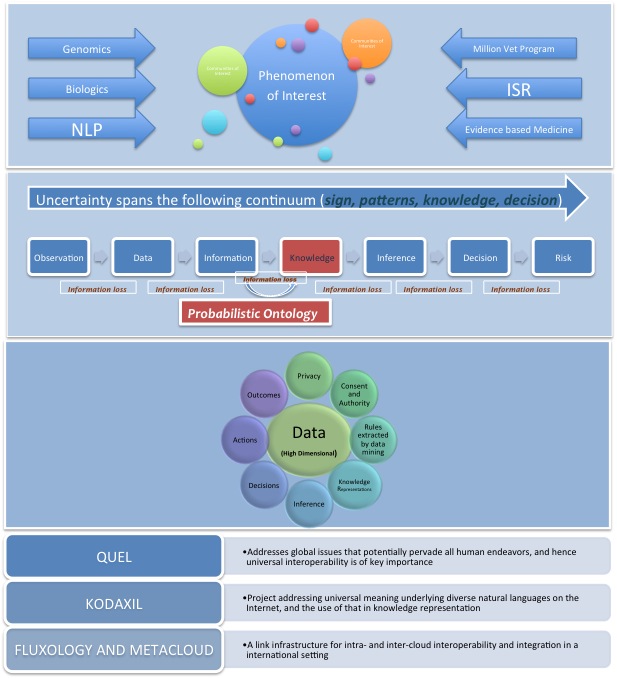
- Q-UEL (Probabilistic Inference + Phenomenon Of Interest): Addresses global issues that potentially pervade all human endeavors, and hence universal interoperability is of key importance
- (Inference Engine + Semantic Inferencing): Project addressing universal meaning underlying diverse natural languages on the Internet, and the use of that in knowledge representation
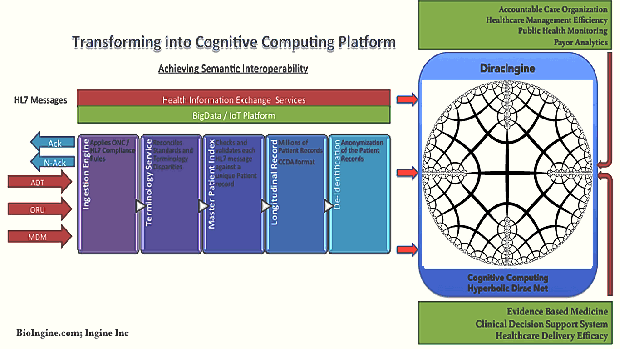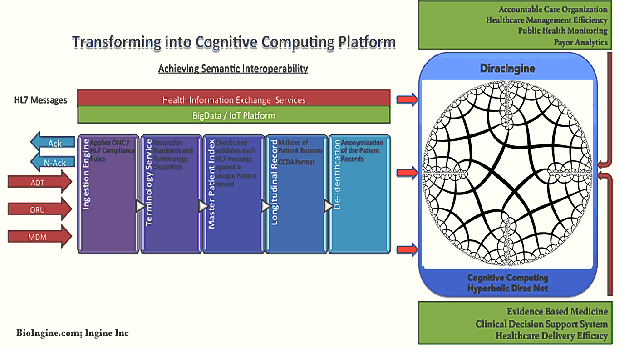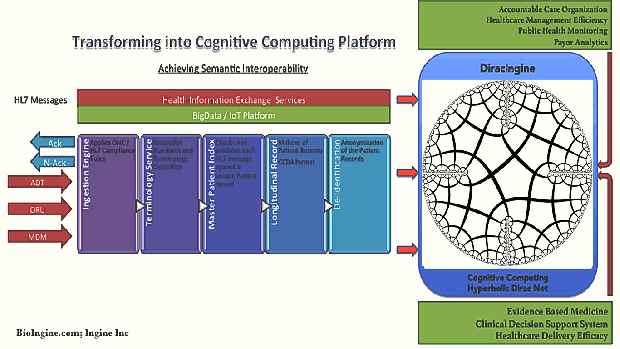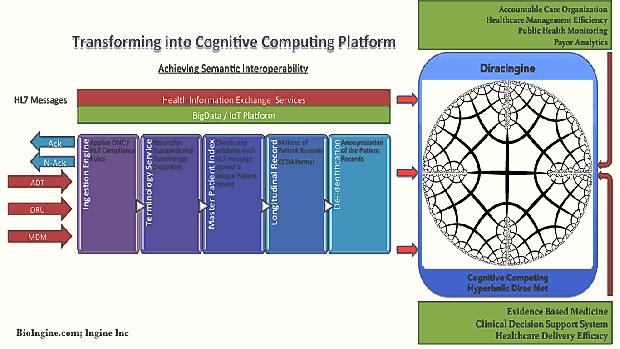
- Inference Engine + Decentralized Infra: A link infrastructure for intra- and inter-cloud interoperability and integration in a coherent high level “metaware” environment. This component can also be explored to be replaced with simpler industry ready solutions such as MarkLogic® Enterprise NoSQL Database on Hadoop Distributed File System.
In an endeavor of this kind the partitions-of-work are inevitably artificial; it is important that this does not impede the integrity of optimal solutions. The most important aspect in The QEXL Approach is, in essence where architecturally Probabilistic Inference (PI) and Data Architecture for the Inference Engine (IE) is designed to be cooperative; software robots are created while PI and IE interact; and the inference knowledge gained by the PI and IE provide rules for solvers (robots) to self compile and conduct queries etc. This is therefore the grandeur of the scheme: This approach will have facilitated programming by nice compilers so that writing the inference network is easy, but it is not required to write the inference net as input code to compile, with the exception of reusable metarules as Dirac expressions with variables to process other rules by categorical and higher order logic. The robots are designed and programmed to do the remaining coding required to perform as solvers. So the notion of a compiler disappears under the hood. The robots are provided with well-formed instructions as well formed queries. Once inferences are formed, different “what – if” questions can be asked. Given that probability or that being the case, what is the chance of… and so on. It is as if having acquired knowledge, Phenomenon Of Interest (POI) is in a better state to explore what it means. Hyperbolic Dirac Networks (HDNs) are inference networks capable of overcoming the limitations imposed by Bayesian Nets (and statistics) and creating generative models richly expressing the “Phenomenon Of Interest” (POI) by the action of expressions containing binding variables. This may be thought of as an Expert System but analogous to Prolog data and Prolog programs that act upon the data, albeit here a “probabilistic Prolog”. Upfront should be stated the advantages over Bayes Nets as a commonly used inference method, but rather than compete with such methods the approach may be regarded as extending them. Indeed a Bayes Net as a static directed acyclic conditional probability graph is a subset of the Dirac Net as a static or dynamic general bidirectional graph with generalized logic and relationship operators, i.e. empowered by the mathematical machinery of Dirac’s quantum mechanics.
The QEXL Approach Theory :- Robson Quantitative Semantics Algebra (RQSA)
Developed by Dr. Barry Robson
Impact Of The QEXL Approach
Impact of The QEXL Approach creating Probabilistic Ontology based on Clifford-Dirac algebra has immense opportunity in advancing the architecture to tackle large looming problems involving System of Systems; in which vast uncertain information emerge. Generally, as such systems are designed and developed employing Cartesian methods; such systems do not offer viable opportunity to deal with vast uncertain information when ridden with complexity. Especially when the context complexity poses multiple need for ontologies, and such a system inherently defies Cartesian methods. The QEXL Approach develops into an ecosystem response while it overcomes the Cartesian dilemma (link to another example for Cartesian Dilemma) and allows for generative models to emerge richly expressing the POI. The models generatively develops such that the POI behavior abstracted sufficiently lend for the IE and the Solvers to varieties of studies based on evidence and also allows for developing systemic studies pertaining to Complex Adaptive System and Complex Generative Systems afflicted by multiple cognitive challenges. Particularly, The QEXL Approach has potential to address complex challenges such as evidence based medicine (EBM); a mission that DoD’s Military Health System envisions while it modernizes its Electronics Health Record System – Veterans Health Information Systems and Technology Architecture (VistA). Vast potential also exists in addressing Veteran Administration’s (VA) Million Veteran Program (MVP); an effort by VA to consolidate genetic, military exposure, health, and lifestyle information together in one single database. By identifying gene-health connections, the program could consequentially advance disease screening, diagnosis, and prognosis and point the way toward more effective, personalized therapies.
Although The QEXL Approach is currently targeted to the healthcare and pharmaceutical domains where recognition of uncertainty is vital in observations, measurements and predictions, and probabilities underlying a variety of medical metrics, the scope of application is much more general. The QEXL Approach is to create a generic multivariate architecture for complex system characterized by Probabilistic Ontology that employing generative order will model “POI” facilitating creation of “communities of interest” by self-regulation in diverse domains of interest, requiring integrative of disciplines to create complex studies. The metaphor of “Cambrian Explosion” may aptly represent the enormity of the immense possibilities in advancing studies that tackle large systemic concerns riddled with uncertain information and random events that The QEXL Approach can stimulate.

The inference engine can be conceptualized into solutions such as MarkLogic NoSQL + Hadoop (HDFS). http://www.marklogic.com/resources/marklogic-and-hadoop/
It is interesting to note that in the genesis of evolving various NoSQL solutions based on Hadoop few insights have emerged related to need for designing the components recognizing their cooperative existence.
The Goal of The QEXL Approach: Is all about Contextualization
The goal employing The QEXL Approach is to enable the realization of cognitive multivariate architecture for Probabilistic Ontology, advancing the Probabilistic Ontology based architecture for context specific application; such as Healthcare. Specifically, The QEXL Approach will develop PI that helps in the creation of generative models that depicts the systemic behavior of the POI riddled with vast uncertain information. Generally, uncertainty in the vast information is introduced by the System of Systems complexity that is required to resolve multiples of ontologies, standards etc., these further introduce cognitive challenges. The further goal of The QEXL Approach is to overcome such challenges, by addressing interoperability at all levels, including the ability to communicate data and knowledge in a way that recognizes uncertainty in the world, so that automated PI and decision-making is possible. The aim is semiotic portability, i.e. the management of signs and symbols that deals especially with their function and interactions in both artificially constructed and natural languages. Existing systems for managing semantics and language are mostly systems of symbolic, not quantitative manipulation, with the primary exception of BayesOWL. RQSA, or Robson Quantitative Semantic Algebra by its author Dr. Barry Robson, to distinguish it from other analogous systems, underlies Q-UEL. It is the development of (a) details of particular aspect of Dirac’s notation and algebra that is found to be of practical importance in generalizing and correctly normalizing Bayes Nets according to Bayes Theorem (i.e. controlling coherence, which ironically Bayes Nets usually neglect, as they are unidirectional), (b) merged with the treatment of probabilities and information based on finite data using the Riemann Zeta function that he has employed for many years in bioinformatics and data mining (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GOR_method), and (c) the extension to more flavors of hyperbolic imaginary number to encode intrinsic “dimensions of meaning” under a revised Rojet’s thesaurus system.
The Layers of the Architecture Created by The QEXL Approach
Layer 1- Contextualization: Planning, Designing driven by Theories
A. Probabilistic Ontology creating Inferencing leading into Evidence Based Medicine
i. Aspects addressed by Q-UEL Tags and Kodaxil Inferencing
- Autonomy / Solidarity
- Inferencing (Kodaxil and Q – UEL)
- MetaData
- Security / Privacy
- Consented vs Un-consented Data
- Creating Incidence Rule (predicated – Q-UEL and Kodaxil)
ii. Kodaxil:- Enforcing Semantics across data sources (global text and data interoperability) – universal meaning underlying diverse natural languages on the Internet
iii. Fluxology:- Logical Meta Data Cloud (A link infrastructure for intra- and inter-cloud interoperability and integration in a international setting)
- Adaptive
- Emergent Data Usage Patterns (networks of networks – enables by Probabilistic Ontology rules)
- Modeless Emergent Hierarchies
- Federation and Democratization Rule for Data (contract, trust, certificates, quality)
B. Development of Probabilistic Model Representing Universal Abstraction of Phenomenon Of Interest
C. Targeting Architecture to Application
- Evidence Based Medicine
- Genomics
- Systemic Healthcare Studies
- etc
Layer 2 – A: Operational Architecture (Logical )
A. Reference Architecture
- Business Con Ops (Use cases)
- Conceptual Target Solution Architecture
Layer 2 – B: Data Management – Data Ingestion and Processing
- The processing of entries in the source data into form suitable for data mining
- The data mining of that processed data to obtain summary rules
- The capture of the appropriate released summary rules for inference
B. Data Storage and Retrieval, Transactions
- Secure Storage and Retrieval
- Enable Secure Transactions
- Secure Data Exchange among several stake-holders and data owners
C. Data Lifecycle, Data Organization Rules, Data Traceability to the Events,
- Security and privacy by encryption and disaggregation of the EHR in a manner that is balanced against authorized access for extraction of global clinical and biomedical knowledge.
- Mechanisms for fine-grained consent permitting sharing and data mining.
- Mechanisms for secure alerting of patient or physician by backtrack when an authorized researcher or specialist notes that a patient is at risk.
- Structure and format that allows all meaningful use cases to be applied in reasonable time, including large-scale data mining.
- Assemblies across sources and data users forming contextual work patterns
- Hardened Security Framework
D. Large EHR repository scaling
E. Data Mining Rules
F. Extracting and creating Incidence Rules
G. Experimenting, observing and creating Semantic Inferences
H. Visualization
You must be logged in to post a comment.